
• Deficiency of many vitamins, includingVitamin D deficiency There isRelated to depression
• low levels of vitamin D mightAffects emotional control Decision making and behavior
• WiTamindee is not a medicine for treating depression. But compensation for vitamin D in people with low levels may play a role.Helps to control emotions andIncrease sleep qualitycan
Treating depression using medication along with psychotherapy. There is a 76-85% success rate (WHO 2020), but the problem is that fewer than 25% patients receive treatment. And there is another part that doesn't want to take medicine. Because of fear of addiction to drugs Or maybe because they can't stand the side effects. [1]
Because depression is a chronic disease, whichCan come back again Especially those who do not receive treatment continuously. It was found that there was a higher rate of recurrence. Therefore, efforts began to be made to look for factors. or other combination methods of treatment Especially in terms of nutritional status, nutrients or vitamin supplements. [2]
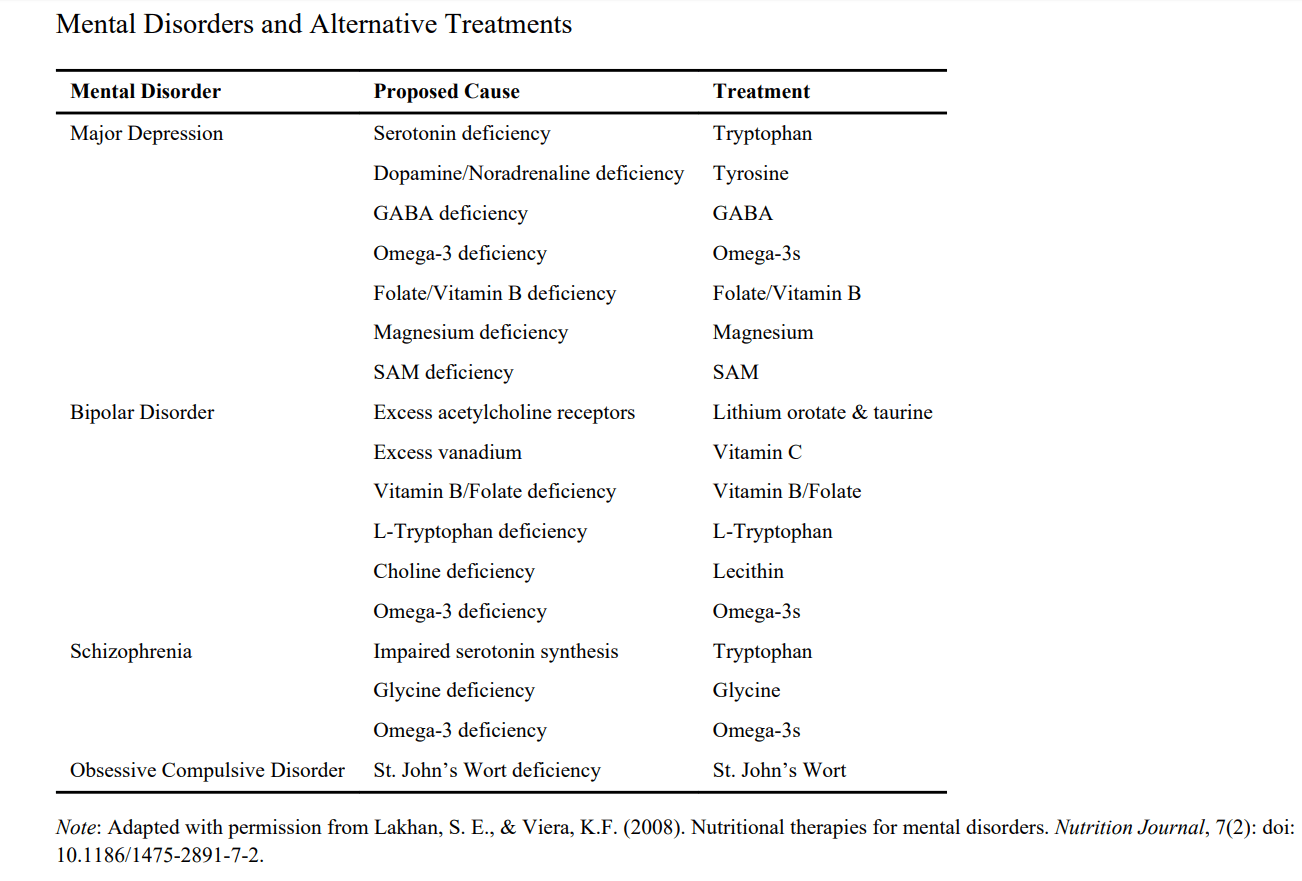
We are starting to have more and more research. that found a relationship between the deficiency of many vitamins, nutrients, or minerals and depression, such as vitamin B3, vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, folate, vitamin D, Zinc, Copper, Magnesium, including essential fatty acids such as Omega-3 or even some amino acids such as GABA, glycine, tryptophan or tyrosine, etc. [3,4,5,6]
A large study of over 31,000 people found thatPeople who were depressed had lower vitamin D levels. significantly controlled group And it was also found that the group that was low in vitamin D There were more people who were depressed in the high vitamin D group. 121% concluded that low vitamin D levels were indeed related to depression.[7]
This is because we find many vitamin D receptors in the brain. Therefore, it was found that in addition to the effect on emotional well-being, Vitamin D deficiency also affects thinking, reading, memory, and brain performance. in many aspects It also affects abnormal behavior, balance (Ataxia), and many other movement disorders.
This is because vitamin D is a vitamin stored in fat. And the brain is a large piece of fatty tissue. We also find vitamin D receptors in almost every brain cell. Especially in the hypothalamus.[8] which is important to the endocrine system which connects the hormonal system of almost every system in the body If looking at both structure and function Therefore, it can be considered that Vitamin D is a hormone. One important thing on the functioning of the nervous system and brain
Epidemiological research has found that Vitamin D is also important for brain development in the womb. Children born to mothers with low vitamin D levels Changes will be found in both the structure and function of the brain. The function of the neurotransmitter dopamine and can increase the risk of schizophrenia in teenagers[9,10]
In addition to vitamin D, Functional Medicine also has Vitamin balance test There are many other types along with testing. The balance of organic acids in the urine (Urine Organic Acids) in order to gain in-depth information. both neurotransmitter balance (Neurotransmitter balance), intestinal microbial balance (Bacterial & Yeast Dysbiosis Markers) and environmental toxin levels. (Environmental Toxicity) to be used to plan adjustments to both main and compensatory foods.Individual nutritional supplements which can determine the size of vitamins type of protein or essential amino acids precisely To help balance neurotransmitters in the brain more efficiently.
1. WHO Factsheet, Depression (2020)
2. Vitamin D and Depression: Where is all the Sunshine, Issues Ment Health Nurses (2010)
3. Association between folate, vitamin B (6), and vitamin B (12) intake and depression in the SUN cohort study. Journal of Human Nutrition & Dietetics (2009) PMID: 19175490
4. Dietary intake of folate, other B vitamins, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in relation to depressive symptoms in Japanese adults. Nutrition (2008) PMID: 18061404
5. Nutrition and depression: Implications for improving mental health among childbearing-aged women. Biological Psychiatry (2005) PMID: 16040007
6. Nutritional therapies for mental disorders. Nutrition Journal (2008) PMID: 18208598
7. Vitamin D deficiency and depression in adults: systematic review and meta-analysis, The British Journal of Psychiatry (2013) PMID: 23377209
8. Distribution of the vitamin D receptor and 1 alpha-hydroxylase in human brain. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy (2005) PMID: 15589699
9. Developmental vitamin D deficiency causes abnormal brain development, Psycho-neuroendocrinology (2009) PMID: 19500914
10. Developmental vitamin D deficiency and risk of schizophrenia: a 10-year update, Schizophrenia Bulletin (2010) PMID: 20833696
Cancer, as we all know, is a non-communicable disease. But it is the disease that causes the greatest loss rate. And currently we can Cancer screening
Herpes vs. Shingles It is a disease caused by a viral infection. A group called Herpes virus
Many people may have heard of NK Cell Therapy.